Written by
Jonathan Taylor
Published on
Apr 20, 2025
What is Generative Engine Optimization?
Few digital marketing channels are as talked about as Generative Search Engine Optimization (GEO) or LLM SEO. The reason so many people are getting excited about GEO is because there's a clear match between user intent, the queries they use, and the benefits of being among those cited in responses. Not to mention that ChatGPT is now recognized as one of the top 10 most visited websites in the world.
LLM tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity and others may seem to operate in the same way as search engines. A user enters a query and gets a result that ideally helps resolve their question. However, there are key differences between how LLMs work and how search engines function—from ranking content to selecting sources for responses, as well as the foundational user expectations.
A citation from an LLM carries much more weight than a typical Google search result. If your prospective buyer is looking for information and you show up in a list of recommended tools, users tend to take that more seriously. The result is more qualified opportunities coming in from these platforms.
In my own experience with clients, we're seeing an increase in the number of ChatGPT and Perplexity referrals. Anecdotally, these referrals are higher quality and much more likely to turn into qualified opportunities. This is fascinating because it means that LLMs are able to pre-qualify and make personalized recommendations.
However, just like SEO before it, getting a citation is not automatic. It requires a strategic, thoughtful approach, but doing so can result in significant benefits for your business. In this article, we'll cover the foundation of what Generative Engine Optimization is and how you can optimize for it.
What is Generative Engine Optimization?

What is Generative Engine Optimization?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a strategy of optimizing your content, both on-site and off-site, to be cited and indexed by LLMs like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini.
GEO is a close cousin to SEO. Many of the same factors are involved in optimizing for LLMs, such as using Schema markup and creating high-quality content that answers users' questions. The differences between SEO and GEO are subtle, but important enough to consider GEO as its own category.
Generative Engine Optimization focuses on factors such as your ability to match user queries, provide valuable content for citation, and ensure both technical web factors and content strategy align with what users may ask of LLMs. GEO also shares a similar challenge to SEO in that it's nearly impossible to know all potential queries users might submit.
The birth of long-tail keywords and "keyword volume zero" in SEO reflects a modern challenge. Users aren't just typing in exact match keywords and hoping to get a robust answer. Queries in both SEO and GEO carry intent and context. For intent, it's important to understand what the user wants from a given query. Because it's impossible to predict all the subtleties behind that intent or variations in how they share that intent, GEO must focus on high-level general intent, much like SEO.
Context is perhaps even more interesting and unique to GEO. LLMs have the ability to understand context and aspects of the user's situation. Some LLMs like ChatGPT store memory over time, which is included in the prompt. The system prompt is sent when somebody asks a question looking for a recommendation or comparing products.
Context is king in this perspective. We're seeing a shift from the search-and-click to an answer-first model. What's remarkable is the level of trust people place in models like ChatGPT and Perplexity. According to recent surveys, 60% of consumers have followed advice given by ChatGPT, and 70% of those found the advice helpful. Product recommendations are among the most trusted advice topics.
This trust is especially significant when you consider that 34% of people say they would trust ChatGPT over a human expert for advice, highlighting a substantial level of confidence in AI-driven recommendations. With 64% of customers open to buying products recommended by ChatGPT or similar technologies, users are taking these product recommendations seriously and acting on them.
How Do You Optimize for LLMs?

Each query to an LLM is unique
Generative Engine Optimization is a relatively new field, but it borrows many principles from Google Search. There is a school of thought that if you're doing good SEO work, this should translate well to GEO. I'd be hard-pressed to disagree with that principle. However, there are definitely nuances to your GEO approach which need to be taken into consideration.
As background, we've completed a study of thousands of citations and hundreds of queries to examine common factors between content that tends to get cited in LLMs. Two major factors in LLM optimization are technical foundations and content characteristics.
Technical Foundations
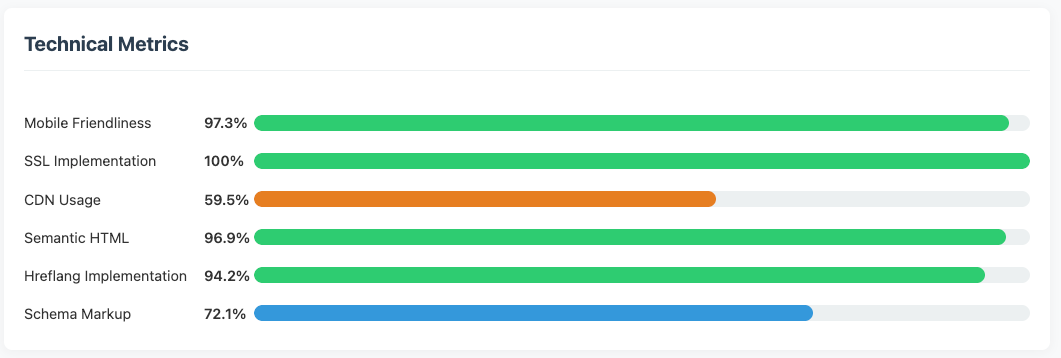
Technical metrics from our analysis
One of the most surprising elements of our research was looking at the technical foundations. We expected that technical elements would be important in LLM optimization and GEO, and our findings backed that up.
As a universal requirement, 100% of the sites we saw cited used SSL (HTTPS), and approximately 97% of them were mobile-friendly. These felt like baseline requirements for any website. Certainly, these translate well from SEO, but it's notable that LLMs, by our account, appear to completely ignore HTTP sites.
Semantic structure—the usage of HTML5 elements like section, article, and so on—also seems to be important. Nearly 96% of the sites we looked at had semantic markup.
Schema or structured data is an important way to communicate what's on a page with search engine crawlers. I always like to think of it as converting on-page content into machine-readable information snippets. These snippets are easily analyzed by search engine crawlers, and it seems LLMs also prefer schema content. We noted that 72% of the citations we saw in our analysis had schema implemented.
To me, this emphasizes schema as an important but not universal factor—certainly an easy win for any website looking to improve their citation rate on LLMs. We've already seen research that validates approaches using bullets and headings help improve LLM presence and frameworks like CFPO become popular.
Content Characteristics
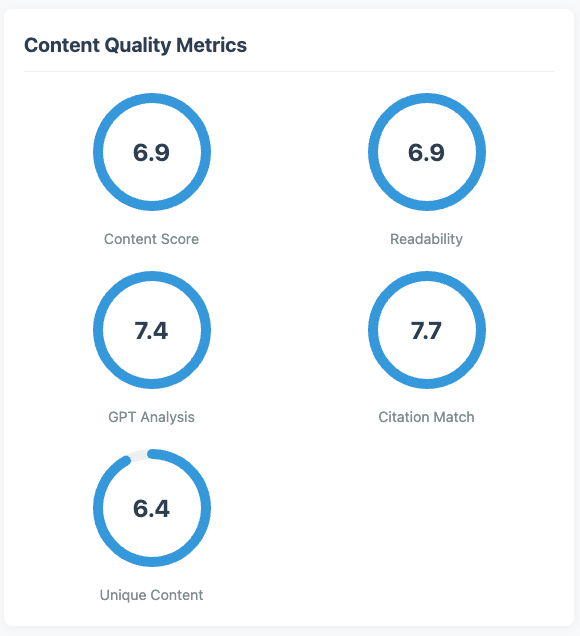
Content quality metrics
In order to get your content cited by LLMs, it's important to write high-quality, relevant content. There is, in my mind, no doubt a window of opportunity for brands looking to create content that is GEO-optimized to fill a gap in current algorithms or in how ChatGPT or Perplexity index content today. Even without a direct link, brand citations can increase branded search volume by 12–18%.
However, accounting for this in the future is not something I would necessarily stake everything on. I think the way that engines look at and evaluate content is going to change considerably over the next few years. We're already seeing new models launching at a rapid pace from various LLM providers such as OpenAI and Claude, so I would expect these engines to become more sophisticated, with a rotation towards higher quality and better context-related content than simply checking off boxes.
Based on our study of thousands of citations, we noticed a few important content characteristics:
First, depth matters. We noticed the average word count of citations was around 2,100 words. This demonstrates LLMs' ability to parse medium-form content and their preference for comprehensive information.
We also scored content quality to see if there were any clear trends in citations. What we noticed is that, by and large, the citation match rate—when we look at the citation resource or link provided against the query we sent—had an average citation rate of 7.66 out of 10, which is pretty solid and indicates that these LLMs are able to match the intent of the query with relevant citations.
One of the other interesting takeaways was the unique content score. We had our AI analyze each piece of content from the citations and give it a score out of ten for uniqueness. Our average score was 6.39. Our expectation was that we would see some unique content, but there appears to be a clustering of somewhat similar content, which may represent an opportunity for individuals and brands to write unique content that gets cited as LLMs potentially start to look for more novelty.
For content type preferences (which could be driven entirely by the queries used), we found that blog content represented nearly 60% of citations, followed by product pages at 27%. This is interesting but definitely related to the type of query. A good tip here is that if you're targeting a very specific type of query, like a product comparison, making sure you have the relevant type of content for those queries is really important.
Strategic Framework for GEO Implementation

Studying GEO strategies
Based on research and experience working with Generative Engine Optimization, it's important to have a strategic framework for your approach. The good news is that much of this approach already overlaps with your current SEO strategy and can be part of the expanded mandate of your search engine optimization team. Certainly, they're the ones most well-suited to target these types of strategies.
We're going to talk about four pillars of this framework: technical foundation, content strategy, authority and attribution, and continuous monitoring.
- Technical Foundation Building
- Content Strategy
- Authority and Attribution Enhancement
- Continuous Monitoring Across Platforms
Technical Foundation Building
While we're still analyzing the underlying data to determine how important factors like site speed, technical optimizations, SEO optimization, semantic markup, and schema markup are, these certainly play a role in LLM rankings. I'm confident to say that things like SSL, mobile friendliness, and semantic HTML are near requirements for ranking in GEO.
If this induces any groans, my point is that these are essential factors for SEO as well. So if your site isn't using these yet, you're already probably suffering on SEO.
Schema markup is an interesting one. Having a strategy for implementing schema markup on your pages with organizational schema is a great first step, but recognizing opportunities to use schema across your site is key. I would look at things like article markup, navigation markup, as well as FAQ markups for B2B brands, and product markup for ecommerce brands. This has merit and potential advantage in the marketplace, and it's certainly good practice.
Content Strategy
I think our approach to content strategy for GEO will ultimately be what is altered the most. The focus on comprehensive content—aiming for higher word counts on key topics—seems to be a factor. Having research sources in your data and blog posts is quite important. We saw that 75.4% of sources cited include some form of research, whether it's third-party research or referencing a report that you built.
Focusing on query matching to your content type will be very important. We did an analysis looking at the types of content, and we found that pillar page style, long-form content tends to rank better than other types of pieces, such as opinion pieces or thinner content. However, there are definitely matches between the types of queries and the type of content you write. For instance, if you're looking for the "best software in 2025," you want a piece on your site that also looks at the top software, ideally ranking yourself along with that so you can benefit from citation. Matching your content to your query will become more important than it was in SEO.
Authority and Attribution Enhancement
One interesting statistic that we looked at was the number of pages that had authorship attribution with them. We found 58.7% of sites had some form of authorship. We also found that most sites included research in their articles, nearly 75% of them.
As mentioned earlier, creating high-quality content that doesn't exist in a vacuum but references other authoritative sources is important. While I'm hesitant to recommend just going to Perplexity and grabbing research from there (because it'll create a self-fulfilling prophecy of sorts by creating links within the same cluster), it could be effective in the short term. I think in the long term, LLMs will search for more novelty to answer user-specific queries.
We haven't talked about off-page factors in this blog post, but I think off-page factors are equally important for authority and attribution. You want to make sure that you have a presence on social media and that you publish elsewhere. Anecdotally, in discussions with folks in my network, I've seen that writing articles on third-party platforms can also increase the likelihood of mentions. For instance, LLMs have a preference toward Reddit and LinkedIn as sources.
Continuous Monitoring Across Platforms
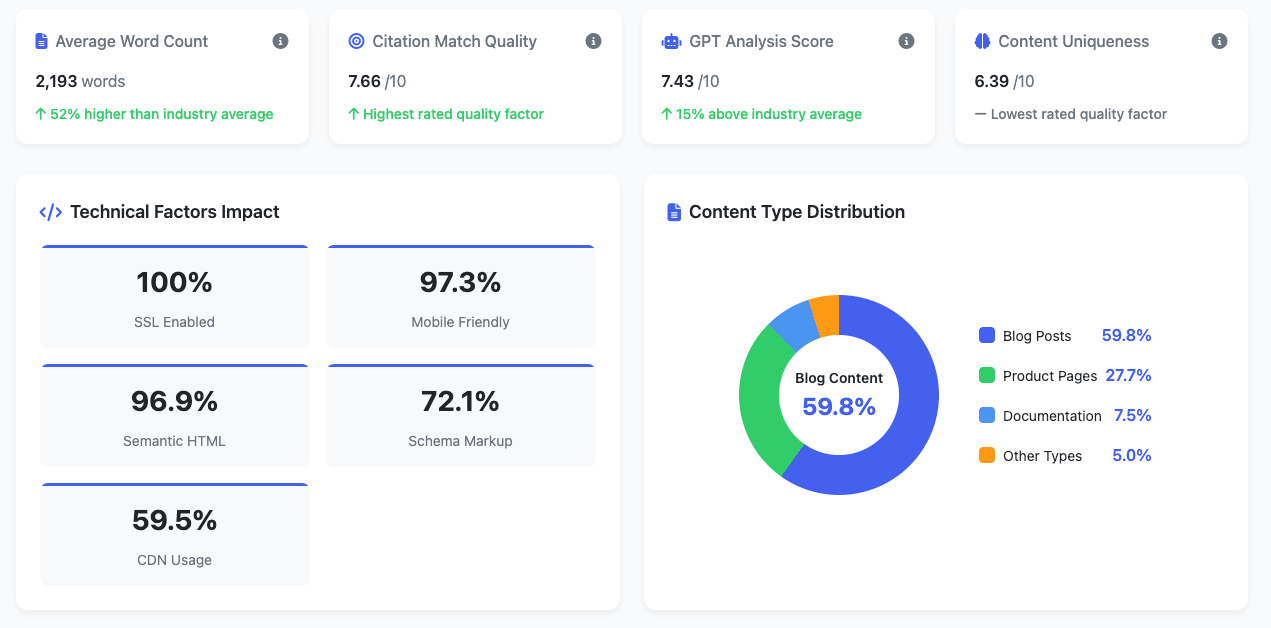
Example of a GEO reporting dashboard
The last piece of the puzzle is your measurement and metrics piece. This is something that is still developing. By large, being able to track citation rates across your different AI systems is key.
There are a couple of points here. First is accounting for the potential variety in queries—each user may phrase things differently, and anticipating all possible combinations and intents behind those queries will be challenging, to say the least.
Next is matching the queries to your keyword strategy. In our study, we looked at exact match queries and then used AI to create prompts to send those queries in a larger prompt form to the various engines. This allowed us to have a parallel approach with our SEO, but still somewhat unique and different.
Another key component of monitoring is checking competitor mentions. Having a defined list of competitors and seeing how often they come up in queries where you would expect to win or would like to have a citation is valuable. If a competitor is there and you're not, you have an opportunity to look at the type of content they've written and then produce something better suited for the LLMs.
Having a robust monitoring strategy is a great first step for many businesses to be able to get a handle on where they land. This includes looking at your web analytics to see how much traffic is coming from these LLMs, as well as making sure that your marketing funnel is able to track opportunities from them. Taking that to the next level with continuous monitoring is a way for you to keep on top of this.
Data-Driven Generative Engine Optimization
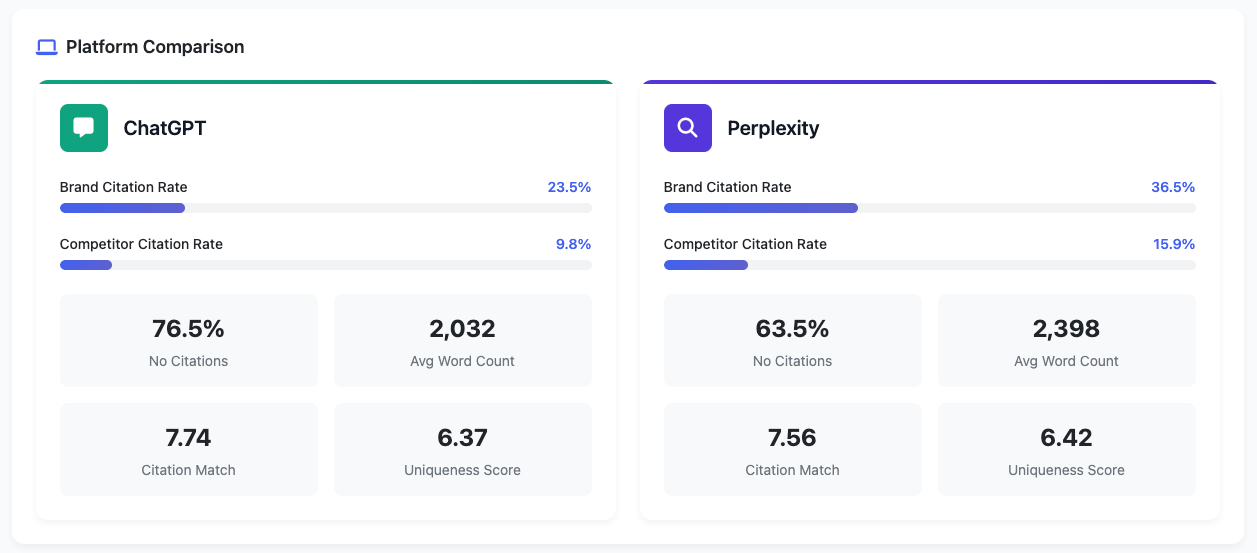
Example of a client dashboard for GEO tracking
The recommendations throughout this article are based on real-world data and citation analysis that we've completed. We've looked at thousands of queries and citations to understand factors like technical rankings, content factors, off-page factors, and on-page factors.
What we've seen, by and large, is that GEO necessitates a revised approach to how you look at content. Search engine optimization services and teams are well-suited to take on the mandate of GEO and are absolutely the right candidates for this.
Having a data-driven approach to your generative engine optimization is a requirement. There is so much opportunity in this space, but without quantifying it and understanding where you can play on these citations, you're missing out on a big opportunity. That's why a linchpin of my GEO services is having citation tracking built in, making sure that we're understanding what citations are coming in for given queries, tracking those queries over time, and identifying where there are gaps for us to fill.
There's an opportunity here for your business to succeed in this brand new area. By working with a GEO service partner like Knowbots, we can help you match queries to content types, identify content gaps, and create a content strategy that helps get you cited in LLMs.
Moving forward, our data-driven approach gives your team the visibility they need into where you stand on LLMs today and a strategic roadmap for winning this marketing channel in the future.


